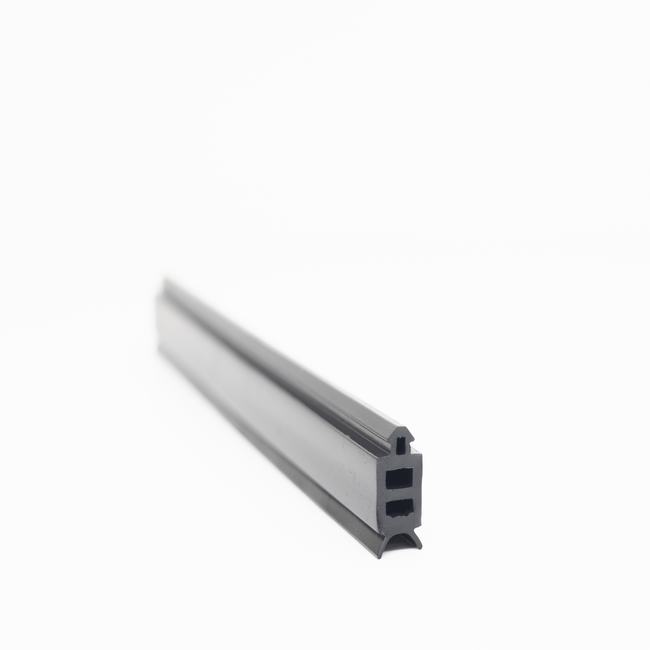
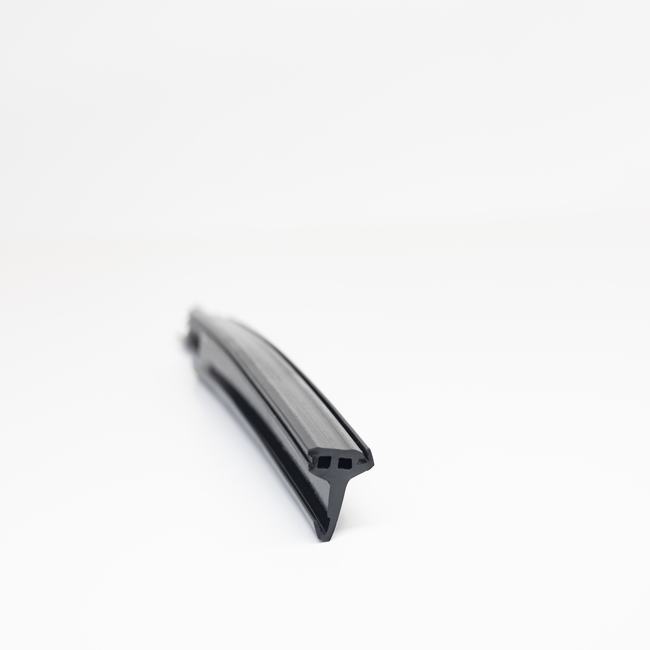
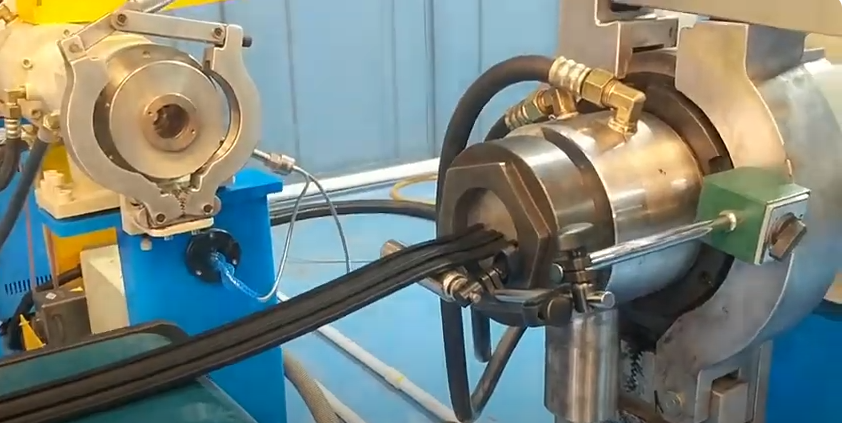
Industrial seals are essential components used in a wide range of industrial applications to prevent the escape of fluids, gases, or contaminants and to maintain the integrity of various systems and equipment. These seals come in various forms, including gaskets, O-rings, packings, and mechanical seals, and they are designed to provide reliable sealing solutions in demanding and often harsh industrial environments. A comprehensive description of industrial seals involves a thorough examination of their various aspects:
- Purpose:
Industrial seals serve several crucial functions in industrial settings, including:
- Leak Prevention: They prevent the escape of liquids, gases, or particles from process equipment, pipes, and machinery, ensuring the safety of personnel and the environment.
- Containment: Seals are vital for containing hazardous or corrosive materials, preventing contamination and damage to equipment.
- Friction and Wear Reduction: In rotating machinery, seals reduce friction and wear, increasing the longevity and efficiency of equipment.
- Temperature and Pressure Control: Seals help control and maintain the temperature and pressure within systems, essential for industrial processes.
- Types:
Industrial seals come in various types, including:
- Gaskets: These are flat or shaped materials, often made of rubber, metal, or composite materials, used to create a seal between two surfaces.
- O-Rings: Circular elastomeric seals commonly used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, offering exceptional sealing capabilities.
- Mechanical Seals: Used in rotating equipment like pumps and mixers, mechanical seals provide dynamic sealing by maintaining a barrier between moving and stationary parts.
- Lip Seals: Employed in rotating shafts to prevent the escape of fluids.
- Packing Seals: Typically used in valves and pumps to create a dynamic seal around a shaft or stem.
- Diaphragm Seals: Employed to separate the measuring instrument from the process media in pressure measurement applications.
- Expansion Joints: These flexible seals accommodate thermal expansion, contraction, and vibration in piping systems.
- Bearing Isolators: Used to protect bearings from contamination and extend their life.
- Materials:
Industrial seals are made from a wide range of materials to suit specific applications. Common materials include:
- Rubber: Such as nitrile, EPDM, and silicone, which provide excellent sealing properties.
- Metal: Used in high-temperature and high-pressure applications, with options like stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloys.
- Plastics: Materials like PTFE, which are resistant to chemicals and high temperatures.
- Composites: Mixtures of various materials, designed to provide specific properties, such as improved sealing and durability.
- Design and Construction:
The design of industrial seals is highly dependent on their intended use. Gaskets, for instance, come in a variety of shapes, such as ring gaskets and sheet gaskets, while O-rings are circular with a round cross-section. Mechanical seals have multiple components, including a rotating and stationary face, and are often lubricated. The construction of seals considers factors like temperature, pressure, chemical compatibility, and the operating environment. - Applications:
Industrial seals are used across various industries and applications, including:
- Oil and Gas: In pipelines, valves, and wellhead equipment to prevent leaks and maintain pressure.
- Chemical Processing: In pumps, reactors, and tanks to contain and control corrosive chemicals.
- Manufacturing: In machinery, hydraulic systems, and air compressors to maintain efficiency and prevent leaks.
- Pharmaceuticals: In equipment for the production and packaging of pharmaceutical products to ensure sterility.
- Food and Beverage: In processing and packaging equipment to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination.
- Aerospace and Automotive: In engines, transmissions, and hydraulic systems to maintain performance and safety.
- Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure the proper functioning of industrial seals. This includes checking for wear, damage, or signs of leakage, and replacing seals that no longer provide an effective barrier.
In summary, industrial seals are fundamental components in various industrial applications, providing sealing solutions that range from static to dynamic. They are available in multiple forms, materials, and designs, tailored to specific industrial needs. Their correct selection, installation, and maintenance are critical to maintaining the integrity, safety, and efficiency of industrial processes and equipment.